.jpg)
Automotive Industry Outlook 2025
Automotive Industry Outlook 2025
Eight key trends empowering automotive companies to navigate industry disruption with decisive transformation and competitive advantage.
Strategic Inflection Point: Navigating the Cycle's Critical Juncture
As we enter 2025, the automotive industry—synced with human history for nearly 150 years—is undergoing profound transformations.
Looking back at 2024, the global auto market navigated waves of disruption and competition. In China, the intensifying price war in the NEV sector drove automakers to seek international expansion. In Europe, subsidy reductions triggered a sharp sales decline, prompting the EU to erect tariff barriers that heightened trade tensions. Meanwhile, in the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act injected substantial subsidies into domestic EV makers, reinforcing protectionist policies that sparked strong global reactions.
Yet, the NEV sector has demonstrated remarkable resilience and sustained momentum. Production and sales continue to grow worldwide, with electrification and intelligence shaping the industry's trajectory. In China, NEV penetration surpassed that of traditional fuel vehicles in a single month for the first time, solidifying its leadership in the global market.
2025 marks the final year of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan and the closing chapter of this growth cycle for the NEV industry.
This year, automakers must navigate deep waters: innovation cannot stagnate, value systems must be redefined, and localized supply chains must integrate with global strategies.
This year, bold exploration remains imperative: vehicle forms are evolving, manufacturing paradigms are shifting, and market structures are being reshaped.
Through a strategic lens, Premier examines eight key industry trends for 2025, paired with a retrospective of 2024’s pivotal developments. In a decisive moment for the industry, we provide insights to help automakers refine their strategies, win the critical battle, and seize the future.
DOWNLOADS

Lite Report (73 pages)

SECTION1
NEV Sales Momentum Eases
Hybrid Models Emerge as Key Growth Lever
In 2025, the global new energy vehicle (NEV) market will continue to grow, but the growth rate is expected to slow down, marking the shift from rapid expansion to high-quality development in the industry.
This trend is driven by two key factors: first, the market is approaching saturation, pushing the industry into a phase of competition within existing markets; second, the challenges of transitioning technologies, coupled with consumer uncertainty about the future of electrification, are leading to divergent growth. In Europe and the US, some automakers are scaling back their electrification goals for the next 5 to 15 years to better align with current market needs.
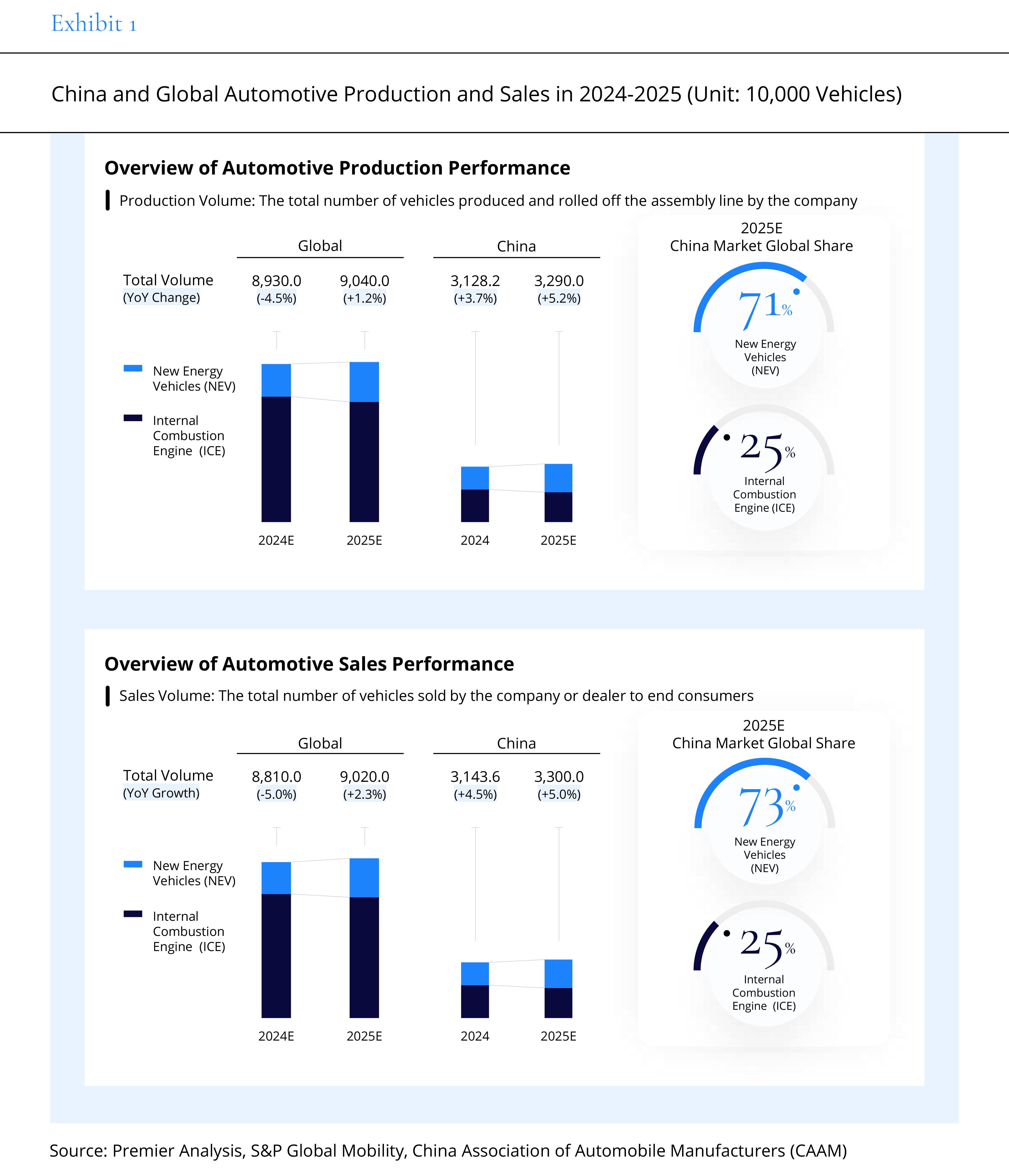
In contrast, China's new energy vehicle market continues to maintain strong growth. It is expected that in 2025, China's car production and sales will reach 32.9 million and 33 million units, respectively, growing by 5.2% and 5.0%, further increasing its global market share and solidifying its leading position.
From a model perspective, hybrid vehicles will become the core driver of growth in the NEV sector. Compared to pure electric vehicles, hybrid models are attracting more and more consumers due to their multiple advantages.
Hybrid vehicles, which do not require large-capacity battery packs, significantly reduce manufacturing costs and provide a lower entry price point amid an intensifying price war among automakers. With rapid advancements in plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) and extended-range electric vehicle (EREV) technologies, these models are gradually reaching or even surpassing pure electric vehicles in terms of power performance, range, and energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the advantage of hybrid vehicles not being overly reliant on charging infrastructure gives them considerable market potential in regions where charging networks are not yet fully developed. These factors will transform hybrids from a "transitional technology" into a mainstream option with long-term competitiveness, opening up new growth opportunities for companies' strategic planning.
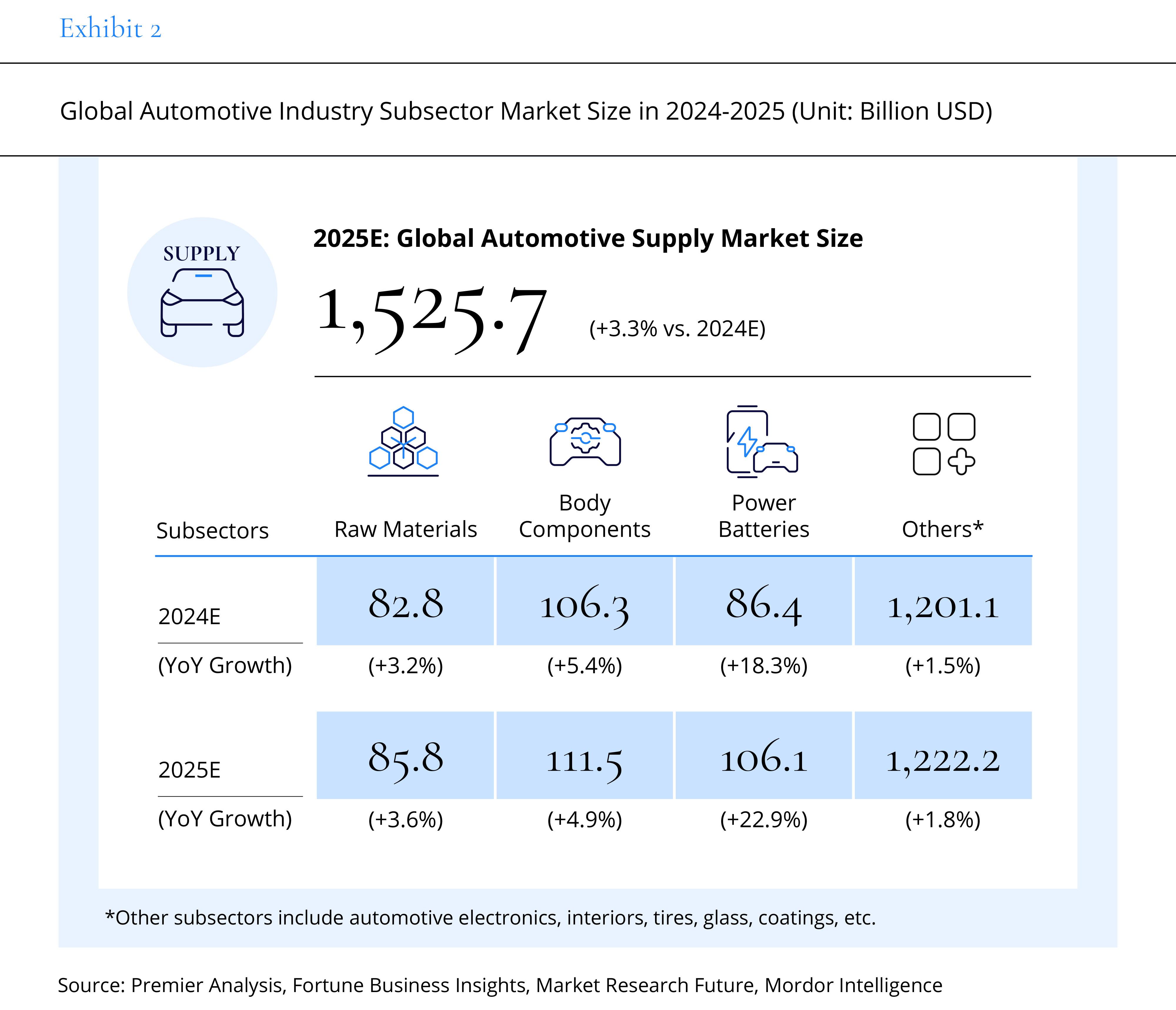
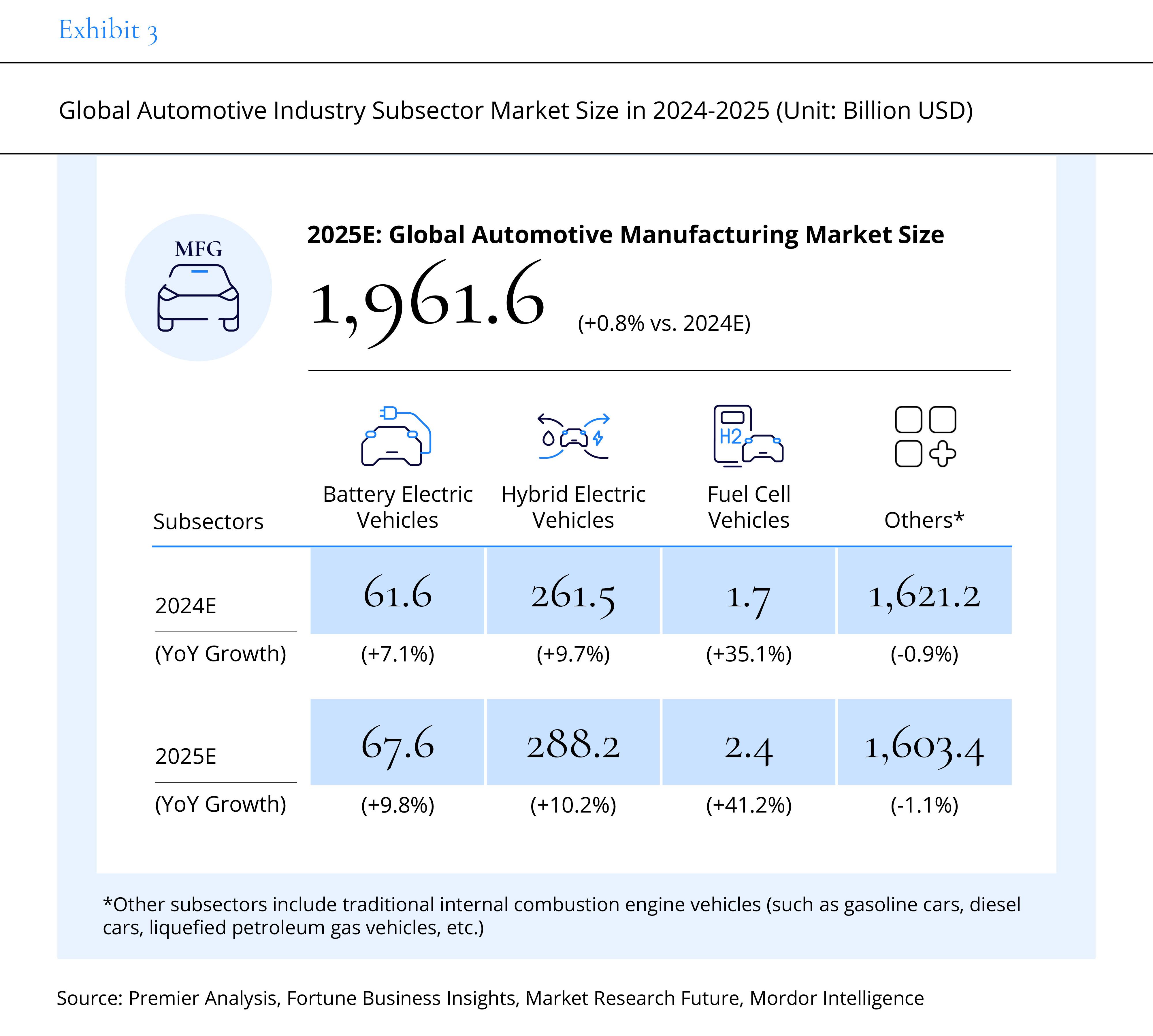
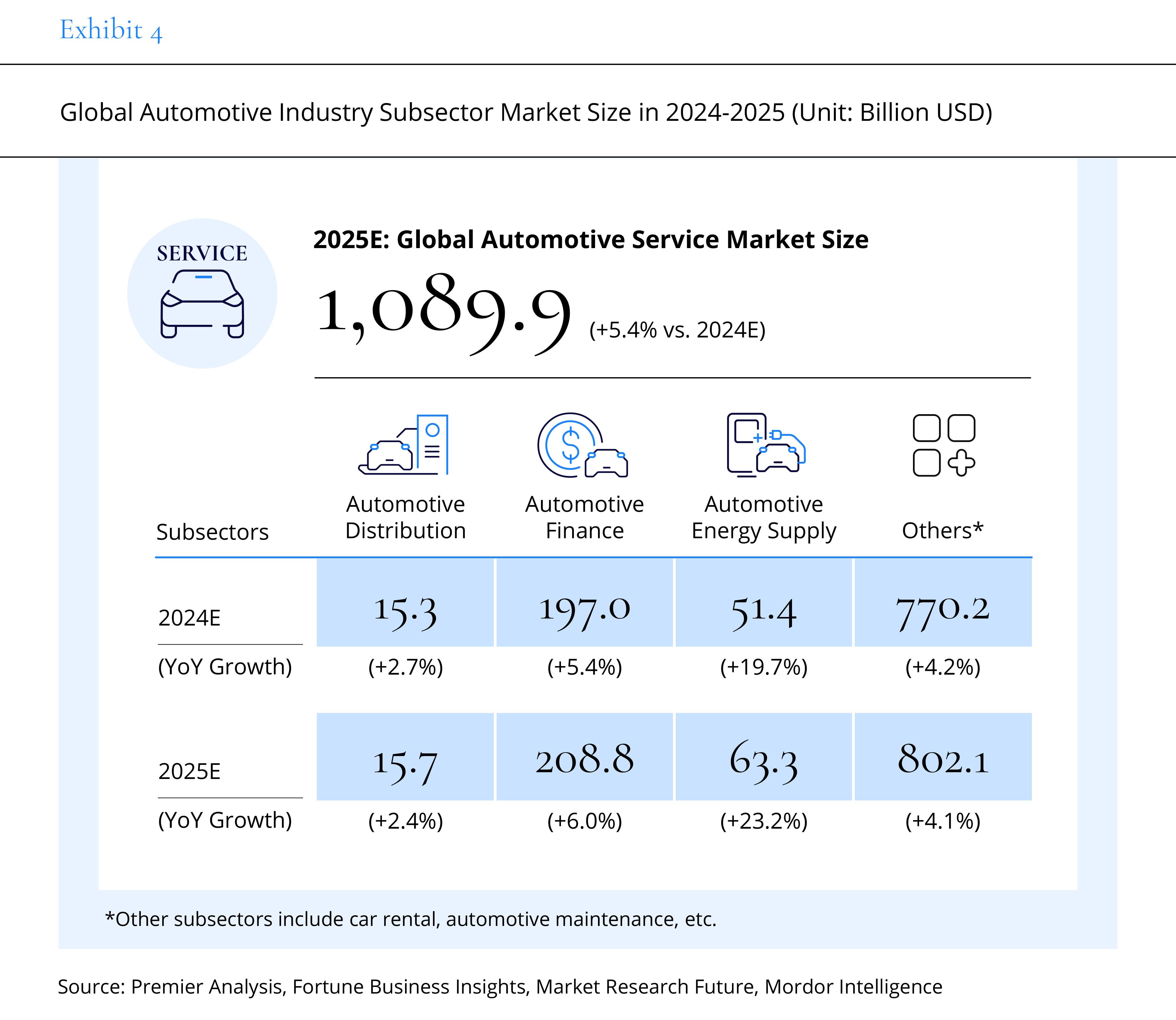
From an industry chain perspective, with the steady development of raw materials, body components, and power batteries, the upstream market is expected to reach $1,525.7 billion in 2025, growing by approximately 3.3%. The midstream market, however, is projected to grow only by 0.8% to $1,961.6 billion, affected by the decline of gasoline vehicles. In contrast, the downstream market, benefiting from the rapid growth of the energy replenishment industry, is expected to reach $1,089.9 billion, with a growth of 5.4%.

SECTION2
Intensifying Trade Frictions Reshape Tariffs
Policy & Regulatory Enhancements Catalyze Industry Upgrades
In 2025, policy-driven shifts in the global automotive industry are expected to continue. Governments worldwide are accelerating the transition toward electrification and intelligent mobility through enhanced NEV incentives, trade tariff adjustments, and regulatory advancements in autonomous driving, exerting a direct and profound impact on industry development and market competition.
Industrial policies will serve as a key driver of transformation. Governments are not only incentivizing consumers to purchase NEVs through subsidies and financial benefits but are also increasing support for both traditional automakers and emerging EV manufacturers. Funding initiatives and policy incentives are expediting the transition to new energy while fostering technological innovation.
Automakers will benefit from these policies, gaining greater autonomy in research and development, particularly in critical areas such as electrification and intelligent driving. Furthermore, countries around the world are actively promoting supply chain localization, strengthening domestic production capabilities to reduce external dependencies and ensure supply chain security and stability.
Changes in global trade tariff policies, particularly escalating trade frictions among major economies, will significantly impact cross-border automotive production and the supply of key components. These trade frictions are not solely driven by trade deficits but are rooted in deeper strategic competition over technology, market access, and industrial chain control.
Moreover, competition among major economies extends beyond trade tariffs to include anti-subsidy measures, intellectual property protection, and other strategic maneuvers, potentially exposing multinational corporations to greater policy risks in different markets and reshaping the global automotive industry's competitive landscape.
At the same time, governments are continuously refining laws and regulations covering various aspects such as vehicle emissions and driving safety.
In response to climate change and environmental pressures, stricter emission standards have been introduced, requiring automakers to rigorously control carbon emissions in the design and production process to meet sustainability targets.
In the autonomous driving sector, regulatory frameworks concerning safety and liability are gradually maturing. Automakers must adhere to increasingly stringent legal requirements throughout research, development, and production to ensure the safety and compliance of their products and services.
Finally, with the growing number of end-of-life batteries, more countries are expected to introduce legislation on vehicle and battery recycling. Automakers will be required to establish recycling and circular economy mechanisms to reduce environmental pollution and promote resource reutilization, ensuring the industry's long-term sustainability.
SECTION3
Globalization Imperative for Chinese Enterprises
From Capacity Deployment to Full-Value Chain Integration
Major markets such as Europe and the United States are imposing differentiated tariff barriers and stringent industry entry thresholds in an attempt to curb the global expansion of Chinese new energy vehicles (NEVs). While Chinese automakers, leveraging their strong cost advantages, can partially offset the impact of tariffs, export restrictions targeting battery electric vehicles (BEVs) remain significant.
To navigate this challenge, some Chinese automakers have adjusted their strategies, shifting the export focus from BEVs to hybrid models. However, this short-term measure does not provide a fundamental solution, especially considering that China's current stronghold markets—such as Russia, Mexico, and the UAE—are relatively limited in size, with short-term growth potential nearing saturation. This creates an urgent need for breakthroughs in high-barrier, high-volume markets like Western Europe and North America.
In response to these constraints, the shift from vehicle exports to overseas production capacity expansion has emerged as the optimal solution for Chinese automakers. By adopting localized production models, including parallel assembly and full-process manufacturing, Chinese automakers are transitioning from a traditional export-driven model to a hybrid trade-and-investment approach. This not only helps reduce tariff costs but also facilitates the establishment of more efficient supply chains and production networks within target markets.
At the same time, the partnership models of Chinese automakers are undergoing a fundamental transformation—from operating independently to forming joint ventures with local enterprises. By integrating capital and production resources, they are creating mutually beneficial ecosystems that help overcome trade barriers and enhance global competitiveness.
However, achieving true internationalization requires more than just product exports. Chinese automakers must expand their global presence across the entire value chain, encompassing brand value, R&D capabilities, supply chain networks, sales and service systems. “Deep localization” will become the key to future competition, demanding not only an adaptation to local cultures and business practices but also the establishment of local R&D centers and supply chain infrastructures in target markets. This approach will drive comprehensive brand and technological integration, ultimately enabling a transition from scaling up exports to enhancing global brand value.

SECTION4
Automaker Shakeout Intensifies
Competing for Secure Market Positioning
In 2024, the automotive industry underwent a major reshuffling. According to Premier’s annual observations, the survival landscape of major automakers and emerging EV startups has diverged significantly, forming three distinct tiers. Among them, 15 companies—including 5 major automakers and 10 startups—maintained stable operations, while 21 companies—12 major automakers and 9 startups—faced significant challenges. Additionally, 6 companies—all startups—were forced to exit the market.
Tier 1 | Strong Breakthroughs, the Stronger Get Stronger
Major automakers such as BYD and Geely have solidified their industry leadership, leveraging strong supply chain integration and in-house battery technology to drive continuous sales growth. Meanwhile, Xiaomi and IM Motors have secured a foothold in the market, benefiting from corporate influence and sustained capital support, showing clear growth momentum.
Tier 2 | Navigating Pressure, Struggling for Survival
Traditional giants like Volkswagen, Hyundai, and BMW, despite their strong industry heritage, have struggled with delays in electrification, leading to declining sales and a sharp drop in profitability, putting them at potential financial risk. Among startups, brands like NETA and Rising Auto face unclear market positioning and insufficient product competitiveness, resulting in weak growth and an urgent need for strategic adjustments and business optimization.
Tier 3 | Market Exit, Silent Departure
Startups such as Jiyue, HiPhi, and Yuanhang failed to establish core product or technological competitiveness, leading to disappointing sales and continuous losses. With funding efforts falling short, these companies ultimately suffered cash flow crises, making it impossible to sustain operations and forcing them out in this round of industry consolidation.

In 2025, the battle for market survival will undoubtedly intensify. The competition between traditional automakers and new energy vehicle (NEV) manufacturers is becoming increasingly fierce. While legacy automakers have deep technical expertise and extensive market experience in the internal combustion engine (ICE) sector, the continued decline in ICE market share is putting immense pressure on their survival.
To maintain market share, many automakers have resorted to price cuts, but this strategy has led to a simultaneous decline in both sales volume and profitability, further squeezing profit margins. In China, the retail share of mainstream joint venture brands has fallen below 30%, while domestic brands are steadily expanding their market presence, creating unprecedented challenges for some of the joint ventures. Previously, brands such as Suzuki, Mitsubishi, and Acura exited the Chinese market due to persistently low sales.
As competition continues to escalate, automakers with low profitability and shrinking market share are expected to be forced out, accelerating the industry's elimination phase.
On the other hand, while EV startups have experienced rapid growth in recent years, with steadily increasing retail market share, many once high-profile companies have still succumbed to market exits and bankruptcies.
Despite their strengths in innovation and technological advancements, scale, capital, and technological reserves remain significant constraints for startups, putting them at a disadvantage when competing against industry leaders like BYD and Tesla. Unlike early movers with strong brand recognition and market dominance, most EV startups lack economies of scale, making it increasingly difficult to sustain growth in an intensely competitive landscape.
How to integrate upstream and downstream resources, secure strong capital support, build differentiated product and technology advantages, enhance overall operational capabilities, and establish a competitive moat through brand loyalty are challenges every emerging EV brand must confront. In the coming years, which brands will successfully break through and secure their position? Time will tell.

SECTION5
Lean Operations & Lifecycle Value Management
Breaking the Spiral of Price Wars
In 2025, the relentless price war shows no signs of easing, leaving no automaker unaffected.
As per-unit profitability continues to shrink, the strategy of relying solely on price cuts to drive sales is no longer sustainable. Automakers must rethink their long-term strategies while navigating the critical transformation driven by electrification and intelligence. This shift demands significant R&D and capital investment, making the pursuit of fully independent development increasingly unrealistic.
In this new landscape, automakers must shift from expansive scale-driven growth to lean operations, refining core competencies, optimizing resource allocation, and making strategic adjustments with a focus on efficiency and results. For example, in capacity management, companies must adopt more flexible strategies, such as capacity-sharing or contract manufacturing, leveraging third-party production facilities or idle capacities from other automakers to reduce upfront investment pressure and enhance resource utilization efficiency.
Furthermore, price reductions alone cannot build a sustainable competitive edge—on the contrary, they risk eroding brand value and causing long-term profit decline. To counter this, automakers must transition from a "single transaction" mindset to a "full lifecycle value management" approach. This means going beyond vehicle manufacturing and sales to explore multi-dimensional value growth opportunities across a vehicle’s entire lifecycle. For instance, companies can develop new business models around battery services, used car circulation, automotive financial solutions, and aftermarket services, leveraging their technological and operational strengths to unlock high-value market segments. By building a diversified, resilient value ecosystem, automakers can establish a sustainable competitive stronghold and secure long-term growth in an increasingly complex market environment.

SECTION6
Synergy of Data, Algorithms, and Computing Power
Fueling Breakthroughs in Intelligent Driving Technology
As 2025 approaches, the automotive industry is transitioning from the first phase of "electrification" to the second phase of "intelligentization." Autonomous driving technology, a key component of this "intelligentization," will benefit from advancements in generative AI, world models, multimodal large models, and in-vehicle intelligent computing platforms, with explosive growth expected this year.
In terms of data collection, generative AI and world models possess the capability to generate high-quality synthetic data, effectively addressing challenges related to data shortages.
Synthetic data offers advantages such as lower collection costs, built-in annotations, and strong cross-platform compatibility. As the deployment of advanced autonomous driving accelerates, AI-generated synthetic data is expected to gradually replace traditional data collection methods, becoming widely used for efficient training and simulation services of autonomous driving models.
For algorithm optimization, the general capabilities of multimodal large models will significantly improve a vehicle’s ability to understand elements such as scenes, obstacles, and navigation information, leading to important breakthroughs in real-time decision-making and control.
It is anticipated that visual-language large model solutions will be adopted by more automakers to enhance existing autonomous driving models, improving the ability to identify and handle rare events in driving environments, and strengthening the robustness and generalization capabilities of autonomous systems for long-tail scenarios.
In terms of computing power, in-vehicle intelligent computing platforms, which provide core support for intelligent driving, will further facilitate technologies such as heterogeneous multi-core high-performance computing, SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture) software architectures, and high-bandwidth in-vehicle communication networks.
Additionally, as the cost of implementing in-vehicle intelligent computing platforms continues to decrease, intelligent driving solutions like NOA (Navigate on Autopilot) are expected to be deployed in more affordable economy models, resulting in exponential growth in market penetration.

SECTION7
Material & Equipment Innovations Take Shape
Solid-State & Smart Batteries Fast-Track Commercialization
As a core component of new energy vehicles, the performance and safety of power batteries have always been a focal point of industry attention.
Currently, traditional liquid lithium batteries, including lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium batteries, are approaching their theoretical performance limits, while solid-state batteries exhibit significant advantages in energy density.
On the other hand, due to the difficulty in measuring internal risk parameters, traditional battery safety management is often in a "black box" state. This has led to a growing demand for intelligent batteries with real-time sensing and self-healing capabilities.
Thanks to the continued efforts of upstream material and equipment suppliers, solid-state electrolytes, cathode and anode materials, as well as equipment for dry electrode, electrolyte pressing and transfer, and diaphragm-free stacking, are now being shipped in bulk and are being integrated with vehicle manufacturers and battery companies for solution development.
Currently, Chinese automakers such as GAC, Changan, and Geely have announced plans for mass production of solid-state batteries, while international automakers like Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, and Toyota are also actively advancing in this field.
However, the manufacturing and usage costs of solid-state batteries remain high. It is expected that the solid-state batteries entering the market in 2025 will be semi-solid or quasi-solid-state solutions. With technological advancements and cost reductions, pure solid-state batteries are expected to enter large-scale deployment by 2027.
Technological advancements in intelligent batteries are also accelerating mass production. The industry is expected to break through challenges related to self-sensing of internal safety parameters and autonomous protection and repair in failure scenarios such as deformation, internal short circuits, and gas generation, significantly enhancing the intrinsic safety of batteries.
Additionally, with breakthroughs in sensing devices and self-healing new materials, intelligent batteries, when integrated, will enable real-time monitoring of battery status, prevent deformation, combustion, and explosion, and facilitate self-repair, effectively addressing the long-standing issue of battery safety in the industry.

SECTION8
A Visionary Future in Convergent Smart Manufacturing
Accelerating Investments in Low-Altitude Economy and Humanoid Robotics
The low-altitude economy and humanoid robotics sectors are gaining significant attention due to their diverse application scenarios and are widely regarded as emerging growth drivers. These fields share strong technological synergies with the automotive industry. In 2024, XPeng AeroHT, Geely Aerofugia, BYD, and GAC Group have all intensified their strategic investments in these areas. As this transformation unfolds, the automotive industry is gradually breaking traditional boundaries, leveraging cross-domain technological integration and the parallel advancement of intelligence and automation to drive industry-wide upgrades. This shift is fostering a new production model and industrial ecosystem, steering the industry toward compound intelligent manufacturing.
The low-altitude economy encompasses urban air mobility (UAM), drone logistics, and emergency rescue operations, emerging as a key frontier for industrial development.
Among these, flying cars play a pivotal role as key enablers of the low-altitude economy. Automakers, leveraging their expertise in intelligent driving, electrification, and propulsion system development, are actively investing in electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, exploring new mobility solutions. Additionally, they are collaborating on industry standards and infrastructure development to support a sustainable low-altitude economic ecosystem.
Currently, XPeng AeroHT has established large-scale production capacity and successfully completed the maiden flight of its modular “Land Aircraft Carrier" flying car. Geely Aerofugia has successfully test-flown its self-developed AE200 LongSky and signed a 120-unit purchase agreement with ICBC Financial Leasing. GAC Group has launched its new flying car brand "GOVY" and plans to introduce a demonstration operation program for flying vehicles by 2027.
At the same time, humanoid robots have emerged as another competitive frontier for automakers due to their extensive potential in automation, service applications, and intelligent interaction.
Intelligent vehicles and humanoid robots share significant technological commonalities—for example, perception, decision-making, and control algorithms used in autonomous driving can be applied to motion control and environmental interaction in humanoid robots. Additionally, precision manufacturing, quality control, and supply chain management capabilities accumulated in automotive production can be leveraged for the development and mass production of humanoid robots.
Leveraging artificial intelligence, mechanical engineering, and sensor technology, automakers are driving the commercialization of humanoid robots in industrial automation and household assistance, strengthening their core competitiveness within the intelligent ecosystem.
Currently, Tesla has officially unveiled the Optimus robot, which is already being used in battery sorting on assembly lines and is planned for consumer sales at a price range of $20,000–30,000. BYD has announced an investment of over ¥100 billion in humanoid robotics and other intelligent technologies, partnering with UBTech to develop a full-stack unmanned logistics solution. BMW has formed a strategic partnership with humanoid robotics company Figure, with the Figure 02 robot completing successful test operations, demonstrating significant performance improvements over its predecessor.

Review & Prospect


.jpg)
Automotive Industry Outlook 2025
Feb 02, 2026
Eight key trends empowering automotive companies to navigate industry disruption with decisive transformation and competitive advantage.
Strategic Inflection Point: Navigating the Cycle's Critical Juncture
As we enter 2025, the automotive industry—synced with human history for nearly 150 years—is undergoing profound transformations.
Looking back at 2024, the global auto market navigated waves of disruption and competition. In China, the intensifying price war in the NEV sector drove automakers to seek international expansion. In Europe, subsidy reductions triggered a sharp sales decline, prompting the EU to erect tariff barriers that heightened trade tensions. Meanwhile, in the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act injected substantial subsidies into domestic EV makers, reinforcing protectionist policies that sparked strong global reactions.
Yet, the NEV sector has demonstrated remarkable resilience and sustained momentum. Production and sales continue to grow worldwide, with electrification and intelligence shaping the industry's trajectory. In China, NEV penetration surpassed that of traditional fuel vehicles in a single month for the first time, solidifying its leadership in the global market.
2025 marks the final year of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan and the closing chapter of this growth cycle for the NEV industry.
This year, automakers must navigate deep waters: innovation cannot stagnate, value systems must be redefined, and localized supply chains must integrate with global strategies.
This year, bold exploration remains imperative: vehicle forms are evolving, manufacturing paradigms are shifting, and market structures are being reshaped.
Through a strategic lens, Premier examines eight key industry trends for 2025, paired with a retrospective of 2024’s pivotal developments. In a decisive moment for the industry, we provide insights to help automakers refine their strategies, win the critical battle, and seize the future.





